Hispanics now make up 22% of all children under the age of 18 in the United States--up from 9% in 1980--and as their numbers have grown, their demographic profile has changed.
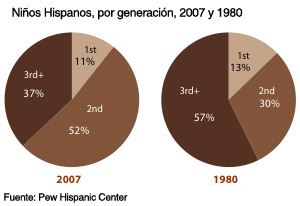
A majority (52%) of the nation's 16 million Hispanic children are now "second generation," meaning they are the U.S.-born sons or daughters of at least
one foreign-born parent, typically someone who came to this country in the immigration wave from Mexico, Central America and South America that began around 1980. Some 11% of Latino children are "first generation"--meaning they themselves are foreign-born. And 37% are "third generation or higher"--meaning they are the U.S.-born children of U.S.-born parents.In 1980, only three-in-ten Latino children were second generation, while nearly six-in-ten were in the third generation or higher. These shifts are noteworthy because many social, economic and demographic characteristics of Latino children vary sharply by their generational status. A Pew Hispanic Center analysis of U.S. Census Bureau data finds that first and second generation Latino children are less likely than third or higher generation children to be fluent in English and to have parents who completed high school. They are more likely to live in poverty. But they are less likely than third or higher generation Latino children to live in single parent households.
Another characteristic that separates Latino children along generational lines is their legal status. Building on earlier research, the Pew Hispanic Center estimates that 7% of all Hispanic children are unauthorized immigrants. But this share varies sharply by generational status. Two-thirds of the 1.7 million foreign-born Hispanic children are unauthorized, while none of the 6 million Hispanic children in the third generation or higher are unauthorized (as the U.S.-born children of U.S.-born parents, by definition they are U.S. citizens at birth). As for those in the middle--the second generation--about four-in-ten have at least one unauthorized immigrant parent and are therefore living in a family whose immigration status is legally mixed.
Projections by the U.S. Census Bureau indicate that by 2025, nearly three-in-ten children in this country will be of Latino ancestry. This report presents findings from several existing and new Pew Hispanic Center analyses of U.S. Census Bureau data.
